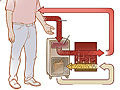
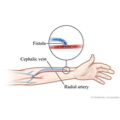
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury (also known as acute renal failure) cause the kidneys to lose their ability to filter and remove waste and extra fluid from the body. Hemodialysis is a process that uses a man-made membrane (dialyzer) to: Hemodialysis for acute kidney injury may be done daily until your kidneys are working again. You are connected to a filter (dialyzer) by tubes attached to your blood vessels. Your blood is slowly pumped from your body into the dialyzer, where waste products and extra fluid are removed. The filtered blood is then pumped back into your body. There are different types of hemodialysis. It can be done in a hospital or center or at home. If it's at home, you do the dialysis yourself, often with the help of a friend or family member. You have choices for how long and how often you do it. You can also do it overnight. Talk about these with your doctor to decide which one might be best for you. Before treatments can start, your doctor will need to create a site where the blood can flow in and out of your body during the dialysis sessions. This is called the dialysis access. The type of dialysis access you have will depend in part on how quickly you need to start dialysis. There are different types of access for hemodialysis: About once a month, you will have blood tests to make sure you are getting the right amount of hemodialysis. These tests are done to help find out how well hemodialysis is working. Your weight before and after each session will be recorded, as will the length of time it takes to complete the dialysis session. If you have hemodialysis at home, you will need to keep records of your weight before and after each session and the length of each session. Hemodialysis is often started after symptoms or complications of kidney failure develop. These may include: Hemodialysis is sometimes used when acute kidney injury develops. Dialysis is always used with extra caution in people who have acute kidney injury, because dialysis can sometimes cause low blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), and other problems that can make acute kidney injury worse. Hemodialysis does not fully replace normal kidney function. It doesn't reverse chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. Hemodialysis only provides up to 10% of normal kidney function. For this reason, it's important to take your medicines as instructed and follow your eating plan. Dialysis is sometimes used to treat an acute kidney injury. It may be used when fluid and electrolyte problems are causing severe symptoms or other problems. Some people who develop acute kidney injury stay dependent on hemodialysis and will go on to develop kidney failure. Most complications that occur during dialysis can be prevented or easily managed if you are monitored carefully during each dialysis session. Possible complications may include: Long-term complications of dialysis may include: Current as of: October 11, 2024 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: October 11, 2024 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Topic Contents
Hemodialysis
Treatment Overview
Access
Things to consider
What To Expect
Learn more
Why It Is Done
How Well It Works
Risks
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Current as of: October 11, 2024 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review BoardHemodialysis
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.