Condition Basics
What is rectal prolapse?
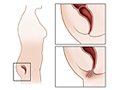
In a rectal prolapse, part or all of the wall of the rectum slides out of place and sticks out of the anus. It may be a:
- Complete prolapse. The entire wall of the rectum slides out of place. At first, it may slip out of the anus only during bowel movements. Over time, this may occur when you stand or walk. And in some cases, the tissue may bulge out of the anus all the time.
- Partial prolapse. The lining (mucous membrane) of the rectum slides out of place. It may slip out of the anus when you strain to have a bowel movement.
Rectal prolapse is most common in older female adults. It sometimes occurs in young children.
What causes it?
The exact cause is not clear, but many things increase the risk of rectal prolapse. These include straining during bowel movements because of constipation. Tissue damage caused by surgery or childbirth, or weak pelvic floor muscles due to aging, may also lead to rectal prolapse.
What are the symptoms?
The first symptoms of rectal prolapse may be:
- Leaking of stool from the anus (fecal incontinence).
- Leaking of mucus or blood from the anus (wet anus).
Other symptoms may include:
- A feeling of having full bowels and an urgent need to have a bowel movement.
- Passage of many very small stools.
- The feeling of not being able to empty the bowels completely.
- Anal pain, itching, irritation, and bleeding.
- Bright red tissue that sticks out of the anus.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history and do a physical exam. This may include checking the rectum for loose tissue and checking how strongly the anal sphincter contracts.
You may need tests to rule out other conditions. For example, you may need a colonoscopy or a barium enema. These may be done to look for tumors, sores (ulcers), or abnormal narrow areas in the large intestine.
How is rectal prolapse treated?
If a rectal prolapse doesn't improve with self-care, you may need surgery. Doctors may attach the rectum to the muscles of the pelvic floor or the lower end of the spine (sacrum). In some cases, they may also remove a section of the large intestine.
Credits
Current as of: October 19, 2024
Current as of: October 19, 2024