Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. This information is produced and provided by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The information in this topic may have changed since it was written. For the most current information, contact the National Cancer Institute via the Internet web site at http://cancer.gov or call 1-800-4-CANCER. Primary liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the liver. Cancer that forms in other parts of the body and spreads to the liver is not primary liver cancer. The liver is one of the largest organs in the body. It has two lobes and fills the upper right side of the abdomen inside the rib cage. The main functions of the liver include the following: Types of liver cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma and bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) are the main types of adult primary liver cancer. Most adult primary liver cancers are hepatocellular carcinomas. This type of liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Primary liver cancer can occur in both adults and children. However, treatment for children is different than treatment for adults. For more information, see Childhood Liver Cancer. Signs and symptoms of liver cancer These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by adult primary liver cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following: Worldwide, liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death. In the United States, rates are highest in American Indian or Alaska Native individuals. Liver cancer is the sixth leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States. Liver cancer causes and risk factors The most common type of liver cancer in adults, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), typically develops in people with chronic (long-lasting) liver disease caused by hepatitis virus infection or cirrhosis. Men are more likely to develop HCC than women. People with multiple risk factors have an even higher risk. Many risk factors have been associated with liver cancer. Not everyone with one or more of these risk factors will develop the disease, and the disease will develop in some people who don't have any known risk factors. Risk factors include the following: Studies have shown there is also an increased risk of liver cancer in people with HBV or HCV infection who use alcohol heavily. Having NASH-related cirrhosis increases the risk of developing liver cancer. Liver cancer has also been found in people with NASH who do not have cirrhosis. Liver cancer prevention Cancer prevention is action taken to lower the chance of getting cancer. By preventing cancer, the number of new cases of cancer in a group or population is lowered. Hopefully, this will lower the number of deaths caused by cancer. Anything that increases your chance of getting cancer is called a risk factor. Anything that lowers your chance of getting cancer is called a cancer protective factor. Prevention includes avoiding risk factors and increasing protective factors. The following are protective factors for liver cancer: Last Revised: 2024-05-15 If you want to know more about cancer and how it is treated, or if you wish to know about clinical trials for your type of cancer, you can call the NCI's Cancer Information Service at 1-800-422-6237, toll free. A trained information specialist can talk with you and answer your questions. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Liver (Hepatocellular) Cancer Prevention: Prevention - Patient Information [NCI]
What Is Liver Cancer?
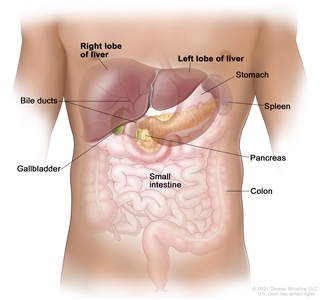
Anatomy of the liver. The liver is in the upper abdomen near the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, and pancreas. The liver has a right lobe and a left lobe. Each lobe is divided into two sections (not shown). Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.Liver (Hepatocellular) Cancer Prevention: Prevention - Patient Information [NCI]



