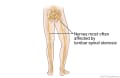
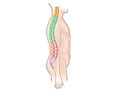
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Laminectomy is the most common type of surgery done to treat lumbar (low back) spinal stenosis. This is also called decompression surgery. This surgery is done to relieve pressure on the spinal nerve roots caused by age-related changes in the spine. It also is done to treat other conditions, such as injuries to the spine, herniated discs, or tumors. In many cases, reducing pressure on the nerve roots can relieve pain and allow you to resume normal daily activities. Laminectomy removes bone (parts of the vertebrae) or thickened tissue that is narrowing the spinal canal and squeezing the spinal nerve roots. A surgeon cuts into your back to do the surgery. In some cases, spinal fusion (arthrodesis) may be done at the same time to help stabilize sections of the spine. Spinal fusion is major surgery, usually lasting several hours. Depending on your health and the extent of the surgery, it may take 2 to 4 weeks to return to work. But if your job requires physical labor, it may take 4 to 8 weeks. Surgery for spinal stenosis is considered when: The decision to have surgery is not based on imaging test results alone. Even if the results of imaging tests show increased pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerve roots, the decision to have surgery also depends on how severe your symptoms are and whether you're able to do normal daily activities. In some cases, spinal fusion will be done at the same time to stabilize the spine. Spinal fusion might make it easier for you to move around (improve function) and relieve your pain. It can also help keep the bones from moving into positions that squeeze the spinal canal and put pressure on the spinal nerve roots. Surgery for spinal stenosis usually is elective. But the doctor might recommend it if symptoms can't be relieved with nonsurgical treatment. Research shows that: But symptoms may return after several years. Some people may need a second surgery if: Spinal fusion may be done at the same time as laminectomy. Spinal fusion may help to stabilize sections of the spine that have been treated with laminectomy. In general, fusion is only done if an area of the spine is unstable. This means that the bones of the spine (vertebrae) move too much or don't move in a normal way. This extra movement causes wear and tear on the nerves or other soft tissues, leading to irritation and pain. The goal of fusion is to keep the damaged bones in the spine from moving so that the soft tissues are protected. Complications from spinal stenosis surgery may depend on what other medical problems you have and how severe your spinal problem is. Also, all surgery poses risks of complications. These complications may be more serious in an older adult. Possible complications include: If you have diabetes or circulation problems or if you smoke, you may be at greater risk for complications. Current as of: July 24, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: July 24, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2026 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Topic Contents
Decompressive Laminectomy for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
What To Expect
Why It Is Done
How Well It Works
Risks
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Current as of: July 24, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review BoardDecompressive Laminectomy for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.