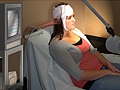
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test that measures and records the electrical activity of your brain. Special sensors called electrodes are attached to your head. They're hooked by wires to a computer. The computer records your brain's electrical activity on the screen. Or it may record the activity on paper as wavy lines. Changes from the normal pattern of electrical activity can show certain conditions, such as seizures. An EEG may be done to: An EEG may be done in a hospital or in a doctor's office. An EEG technologist does the test. The EEG record is read by a doctor who is trained to diagnose and treat problems that affect the nervous system (neurologist). You will be asked to lie on your back on a bed or table. Or you may sit in a chair with your eyes closed. The EEG technologist will attach several flat metal discs (electrodes) to different places on your head. A sticky paste is used to hold them in place. Instead of separate electrodes, you may wear a cap with several fixed electrodes. In rare cases, the electrodes may be attached to the scalp with tiny needles. The electrodes are hooked by wires to a computer that records the electrical activity in the brain. A machine can show the activity as a series of wavy lines on a piece of paper. Or the activity may be shown as an image on the computer screen. You will need to lie still with your eyes closed during the recording. The technologist will watch you directly or through a window during the test. The recording may be stopped from time to time. This allows you to stretch and change your position. The technologist may ask you to do different things during the test to see what activity your brain does at that time. The time it takes to have the test done varies. A typical EEG takes only about 30 to 60 minutes. But certain EEGs can take an hour or two. Some tests called ambulatory EEGs can take 24 to 72 hours. They can be done at home. There is no pain during an EEG. If needle electrodes are used (which is rare), you will feel a brief, sharp prick when each electrode is put in. It will feel kind of like having a hair pulled out. If electrodes are placed in your nose, they may tickle. If you are asked to breathe fast, you may feel lightheaded or have some numbness in your fingers. This is normal. It will go away a few minutes after you start breathing normally again. An EEG is a very safe test. The electrical activity of your brain is recorded. But no electrical current is put into your body. An EEG is not the same as electroshock (electroconvulsive) therapy. If you have a seizure disorder such as epilepsy, the flashing lights may trigger a seizure. Or a seizure may happen if you hyperventilate. If it happens, the technologist is trained to take care of you during the seizure. EEG test results are ready on the same day or the next day. There are several types of brain waves. Normal: Abnormal: Current as of: October 2, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: October 2, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2026 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Why It Is Done
How To Prepare
How It Is Done
How long the test takes
How It Feels
Risks
Results
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Related Information
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Current as of: October 2, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review BoardElectroencephalogram (EEG)
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.