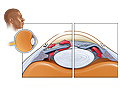
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Glaucoma is the name for a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve. This nerve carries information from the eye to the brain. When the nerve is damaged, you can lose your vision. Glaucoma is one of the most common causes of legal blindness in the world. At first, people with glaucoma may have very mild symptoms. But if the disease isn't treated, vision loss may get worse. It can lead to total blindness over time. There are different types of glaucoma. The exact cause of glaucoma isn't known. Experts think that increased pressure in the eye (intraocular pressure) may cause the nerve damage in many cases. But some people who have glaucoma have normal eye pressure. In open-angle glaucoma, the only symptom you may notice is loss of side (peripheral) vision. You may not notice this until it is serious. Symptoms of closed-angle glaucoma usually happen suddenly and can include severe pain and redness in the eye. In childhood glaucoma, symptoms can include watery eyes and sensitivity to light. Your doctor will ask you questions about your symptoms and do a physical exam. If your doctor thinks you have glaucoma, you will need to see an eye specialist. The specialist will do an eye exam and measure the pressure in your eyes to check for signs of glaucoma. Glaucoma can't be cured. But there are things you can do to help stop more damage to the optic nerve. To help keep your vision from getting worse, you'll probably need medicine (most likely eyedrops) every day. You may also need laser treatment or surgery. You'll also need regular checkups with your eye doctor. If you have vision loss, you can do things to help keep your quality of life. You can use vision aids, such as large-print items and special video systems. Support groups can also help you deal with vision loss. Take your medicines as directed. Make sure to go to all of your doctor appointments. Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health. In open-angle glaucoma, fluid in the eye doesn't drain well. When this happens, the fluid builds up, increases the pressure, and damages the optic nerve. This causes vision loss. But some people who have this type have normal eye pressure. The reason for this is not known. In closed-angle glaucoma, fluid can't drain because the drainage angle is blocked. This can happen when the colored part of the eye and the lens block the movement of fluid. A defect or scar in the eye can also block fluid. In congenital glaucoma, babies are born with it. In infantile glaucoma, it develops in the first years. It can happen because the mother had an infection during pregnancy. Some babies have a family history of the condition. Some people get glaucoma after an eye injury or eye surgery. Some medicines (corticosteroids) may also cause glaucoma. There are some things that can put you at risk for the different types of glaucoma. You have a higher risk for open-angle glaucoma (OAG) if you: You have a higher risk for closed-angle glaucoma (CAG) if you: Your baby has a higher risk for childhood glaucoma if: If you have open-angle glaucoma, you likely won't have any symptoms at first. You may have vision loss, but you may not notice it until the disease has become very serious. Any vision loss is most often side (peripheral) vision loss. Symptoms of closed-angle glaucoma, such as blurred vision, can be mild. But they are often severe and happen suddenly. You may have pain and redness in your eye and see colored halos around lights. Other symptoms include vision loss, feeling sick to your stomach, and vomiting. In congenital and infantile glaucoma, signs can include watery eyes and being sensitive to light. Your baby's eyes may look cloudy or larger than normal. Your baby may rub their eyes, squint, or keep their eyes closed much of the time. Glaucoma usually affects side vision first. With no treatment, vision loss will continue. This will cause total blindness over time. Treatment can't reverse vision loss. But if glaucoma is found and treated early, good eyesight can usually be maintained. With open-angle glaucoma, vision changes so slowly that your eyesight may be affected before you notice it. Blind spots from each side of the field of vision meet little by little, increasing the area of blindness. Central vision is affected last. Closed-angle glaucoma can happen in short episodes over the long term. Or it can happen suddenly (acute). If it's acute, it's an emergency because severe and lasting vision loss can develop soon after symptoms start. Childhood glaucoma may be present at birth or may develop within the first few years of life. Call 911 or other emergency services immediately if you have: Call your doctor if you: When checking for possible glaucoma, your doctor will ask about your past health and do a physical exam. If your doctor thinks you may have glaucoma, he or she will refer you to an eye specialist (ophthalmologist). The specialist will check your eyes to help find out if you have the disease and how severe it is. He or she will look for certain signs of damage in the eye by checking things like: Ophthalmoscopy, gonioscopy, slit lamp exam, and optic coherence tomography all check the structures of the eye. Tonometry measures the pressure in the eye (intraocular pressure, or IOP). Vision tests include tests to check for visual acuity and loss of side and central vision (perimetry testing). Tests such as ultrasound pachymetry measure the thickness of the clear front surface of the eye (cornea). Cornea thickness, along with intraocular pressure, helps determine your risk for glaucoma. Most treatment for glaucoma is done to lower the pressure in the eyes. Treatment depends on the type of glaucoma. If you have glaucoma, you will need regular eye exams and treatment for glaucoma for the rest of your life. If you have vision loss, there are things you can do to help keep your quality of life. It's common to feel sad or angry when you learn that you have glaucoma. Support groups and counseling can also help you deal with vision loss. Your doctor can also refer you to counselors who specialize in helping people adjust to living with low vision. Eye medicines can cause symptoms all through the body. Your medicine may need to be changed. Using them the right way can help reduce side effects. Carry a wallet card or other identification that says that you have glaucoma. Prescription medicines to lower the pressure inside the eye (intraocular pressure, or IOP) are used to treat all types of glaucoma. One type reduces the amount of fluid (aqueous humor) that is produced by the eye. The other type increases the amount of fluid that drains out of the eye. You can use these medicines as eyedrops, as pills, in liquid form by mouth, or through a vein (in emergency situations). In most cases, eyedrops are used first. In childhood glaucoma, medicines may be used to decrease the pressure in the eyes. They also reduce the cloudiness of the clear front surface (cornea) of the child's eye. Medicines are usually used only until surgery can be done. When glaucoma has already caused vision loss, more vision loss may occur even after the pressure in the eye is lowered to the normal range with medicine. Talk to your doctor about the goals of treatment, how long you will try the medicine, and the possible side effects. Eye medicines can cause symptoms all through the body. In most cases, you'll keep taking these medicines for the rest of your life. These include: These include: Surgery for glaucoma reduces the pressure in the eyes by allowing fluid to drain. It opens blocked drainage angles or creates a new opening so fluid can drain. Doctors can use either a surgical cutting tool or a laser to do surgery. Laser surgery is usually tried first. If it doesn't help, your doctor may try conventional surgery. There are three basic types of surgery: Deciding whether to have surgery for glaucoma can be hard. Here are some reasons. Current as of: October 1, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: October 1, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Glaucoma
Condition Basics
What is glaucoma?
What causes it?
What are the symptoms?
How is it diagnosed?
How is glaucoma treated?
What can you do to cope with glaucoma?
Health Tools
Cause
What Increases Your Risk
Symptoms
What Happens
When to Call
Check your symptoms
Exams and Tests
Learn more
Treatment Overview
Self-Care
Learn more
Medicines
Medicines that decrease the amount of fluid produced by the eye
Medicines that increase the amount of fluid that drains out of the eye
Learn more
Surgery
Deciding about surgery for glaucoma
Learn more
Related Information
References
Citations
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Current as of: October 1, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review BoardGlaucoma
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.