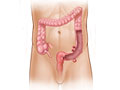
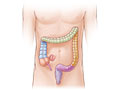
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Diverticulitis is a condition that happens when pouches (diverticula) form in the wall of the colon and then become inflamed or infected. This can cause tenderness, cramps, or pain in the belly. Not everyone who has these pouches gets diverticulitis. Mild attacks may heal on their own. Doctors aren't sure what causes diverticulitis. Bacteria grow in pouches (diverticula) that sometimes form in the wall of the colon. These bacteria can lead to inflammation or infection. Doctors think diverticula form when high pressure inside the colon pushes against weak spots in the colon wall. Belly pain, often in the lower left side, is the most common symptom of diverticulitis. The pain is sometimes worse when you move. Other symptoms include fever, chills, bloating, and gas. You may also have diarrhea or constipation. Symptoms can last from a few hours to several days, or longer if not treated. To diagnose diverticulitis, your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and examine you. You may have tests to see if you have an infection or other problems. The tests may include blood tests or a digital rectal exam. They may also include CT scans, ultrasound, or X-rays of your belly, or other tests. Treatment for mild symptoms of diverticulitis starts with antibiotics, pain medicines, and diet changes. You can try home treatment, such as a heating pad, for pain. To treat serious symptoms, you may need a hospital stay or surgery. Doctors aren't sure what causes diverticulitis. Bacteria grow in pouches (diverticula) that sometimes form in the wall of the colon. These bacteria can lead to inflammation or infection. Doctors think diverticula form when high pressure inside the colon pushes against weak spots in the colon wall. It is not known why some people who have these diverticula get diverticulitis and others do not. In most cases, a diet with good fiber makes stool that is bulky and can move easily through the colon. A low-fiber diet can cause small, hard stools. This means it takes more pressure in the colon to move stools out of the body. This puts more pressure on the walls of the colon. The possibility of having diverticulitis increases with age. You may be more likely to develop diverticulitis if you: Symptoms of diverticulitis include: Symptoms may last from a few hours to several days. They may last longer if the problem isn't treated. Complications also can cause symptoms. If an abnormal opening (fistula) develops between the colon and the vagina or the colon and the urethra, you may pass air or stool from the vagina or the urethra. Diverticulitis occurs when pouches (diverticula) that have formed in the wall of the large intestine (colon) become inflamed or infected. It is not known why some people who have these pouches (diverticulosis) develop diverticulitis and others do not. Mild attacks of diverticulitis, with few symptoms of infection or inflammation, sometimes heal without treatment. In most cases, doctors prescribe oral antibiotics. They may also suggest a clear liquid diet to rest the bowel until it isn't inflamed. When infection and symptoms are severe, diverticulitis is treated in the hospital. Treatment includes antibiotics given in a vein (I.V.) and resting the bowel with I.V. fluids. If symptoms are severe and not treated, problems such as an abscess or fistula may happen. Surgery often is needed to treat these. It is common to have lower belly pain after recovering from an attack of diverticulitis. But this pain doesn't always mean it's returned. Call 911 or other emergency services immediately if the person: Call your doctor now if you have: Call your doctor if you: Call your doctor if you are treating mild diverticulitis at home and: To diagnose diverticulitis, your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and examine you. The doctor may do tests to see if you have an infection or to make sure that you don't have other problems. Tests may include: Treatment depends on how bad your symptoms are. If the pain is mild, you are able to drink liquids, and you have no signs of complications, treatment may include: If the pain is severe, you are not able to drink liquids, or you have complications of diverticulitis, you may need a hospital stay. Treatment will include: Sometimes surgery is needed to treat some problems or repeated attacks. Current as of: October 6, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Current as of: October 6, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review Board This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com. © 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.Diverticulitis
Condition Basics
What is diverticulitis?
What causes it?
What are the symptoms?
How is it diagnosed?
How is diverticulitis treated?
Cause
What Increases Your Risk
Symptoms
What Happens
When to Call
Check your symptoms
Exams and Tests
Learn more
Treatment Overview
Self-Care
Learn more
Related Information
References
Citations
Credits
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein. Current as of: October 6, 2025 Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff Clinical Review BoardDiverticulitis
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.